Technological Trends and Future Directions in DLMS/COSEM
Shwetha Bhat April 9, 2025
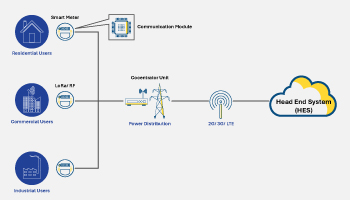
Shwetha Bhat April 9, 2025

A number of technological advancements are defining the future of DLMS/COSEM-based smart metering systems. These trends seek to advance functionality, security, and efficiency and support new applications. This article explores some of the latest advancements:
Integration with IoT (Internet of Things) technologies is one of the emerging trends. IoT connectivity enables smart meters to communicate with home appliances, renewable energy installations, and cloud-based analytics platforms.
Optimized Energy Use: IoT-based smart meters can talk to home appliances to optimize energy use. Washing machines or electric vehicle charging, for instance, can run during off-peak periods in response to real-time electricity rates.
Renewable Energy Integration: Smart meters can synchronize with solar panels and battery storage to maximize energy generation, storage, and use. This optimizes grid stability and encourages decentralized power generation.
Improved Grid Monitoring: Smart meters based on IoT give utilities immediate data, enhancing grid visibility, fault detection, and predictive maintenance.
With growing dependence on digital infrastructure, DLMS/COSEM security mechanisms are continuously developing. High-level encryption, authentication methods, and anomaly detection systems are being implemented to secure smart metering systems against cyber-attacks.
Blockchain Integration: Blockchain technology is also being researched to provide increased data security and transparency. It has the capability to facilitate secure peer-to-peer energy transactions and automatic billing through smart contracts.
AI-Powered Anomaly Detection: Machine learning techniques are being used to identify anomalous patterns of energy consumption, which can signal attempts at fraud or cyber-attacks. Such systems can trigger real-time alarms and automated action.
As grids get more dynamic, DLMS/COSEM is developing to accommodate new features that enhance grid management and consumer engagement.
Microgrid and Virtual Power Plant (VPP) Support: Future releases of DLMS/COSEM with newer OBIS codes and interface classes (ICs) will enable more effective monitoring and coordination of distributed energy resources (DERs). This encompasses the smooth integration of solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage systems into microgrids and VPPs.
Advanced Demand Response Programs: Smart meters will be central to demand-side management by reacting to real-time grid conditions. Consumers can be encouraged to shift their energy consumption in accordance with dynamic pricing and grid load levels.
Electromobility and Smart Charging: DLMS/COSEM is being extended to accommodate electric vehicle (EV) charging stations. This facilitates smart charging strategies that take into account grid capacity, availability of renewable energy, and cost minimization.
To lower data transmission needs and improve responsiveness, new DLMS/COSEM systems are adding edge computing functionality.
Real-Time Data Analytics: Smart meters can process data locally, recognizing consumption patterns and issues without using central servers.
Faster Decision-Making: Decentralized data processing facilitates faster response times for demand response, outage detection, and load balancing.
DLMS/COSEM remains the cornerstone of smart metering, providing a strong and standard method for the management of energy data. However, it still needs to overcome problems such as complexity in implementation, limited bandwidth, incompatibility of devices, and security threats. The future of DLMS/COSEM is to be able to integrate with IoT, increase security, increase its functional scope, and use edge computing to make it more efficient. As the energy industry develops towards higher digitalization and decentralization, further innovations in DLMS/COSEM will continue to keep it relevant in new energy systems.

July 25, 2025
The world energy scene is being revolutionized by the fast-paced increase of decentralized renewable energy sources like rooftop solar, wind microturbines, and energy storage in batteries. batteries. The driving force…
Know More
July 25, 2025
Smart metering has evolved significantly over the last two decades as it became a building block of modern energy management solutions. At the core of the evolution is the DLMS/COSEM…
Know More
July 25, 2025
As the energy sector undergoes rapid digital transformation, smart metering has emerged as a foundational technology in modern utility networks. By enabling real-time monitoring, automated billing, and remote disconnection, smart…
Know More