10 Critical Factors for Successful DNP3 SCADA System Design
Shwetha Bhat February 12, 2025
Shwetha Bhat February 12, 2025
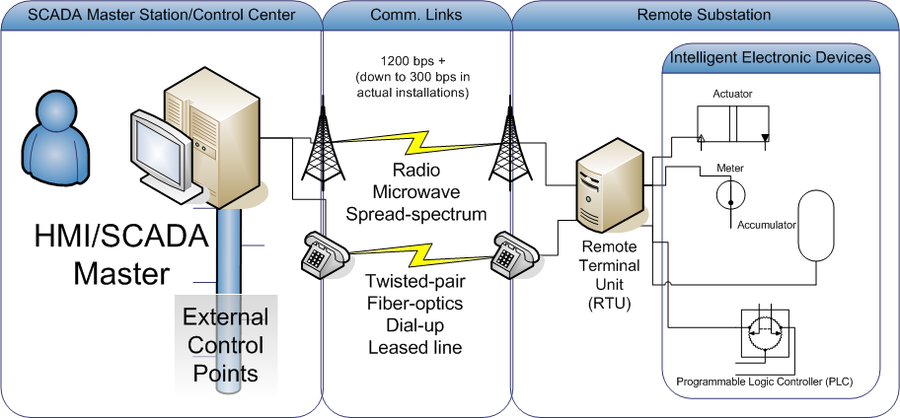
When it comes to the design of a SCADA system that incorporates the use of DNP3 protocol, several factors are influential. These are considered in the design for reliable and efficient operation.
Some of the key factors that influence the design of a SCADA system using DNP3 include:
The general architecture with respect to how master stations, RTUs, and communication routes are distributed has an impact on the design. Several architectures are supported in DNP3, like point-to-point, point-to-multipoint, and multi-drop, all of which impact the network topology and communications strategy.
Network topology comes in star, ring, mesh, or hybrid configurations that define the physical layout and device interconnectivity of a communications network. DNP3 allows for flexible configuration in the creation of topologies but, because of this, requires extra painstaking planning to achieve dependable communication and data integrity.
The designer must be aware of data requirements that are needed by the SCADA system. DNP3 provides several data objects for various types of data points-analog, binary, and counter-actually, one can even define data points if that is what the application requires. The designer must decide on data polling frequency, event reporting requirements, and priority of critical data.
DNP3-based SCADA systems normally operate in an environment where reliability may be regarded as a critical factor. Designing for redundancy at various levels/points-communication links, RTUs, and master stations-can always guarantee availability on system failures/disruptions.
The biggest concern for security in the SCADA system is cybersecurity. DNP3 allows different securities like authentication, encryption, and integrity provided by CRC or cryptographic hashes. Designers should implement these features to avoid unauthorized access and other kinds of cyber threats such as manipulation.
DNP3 is extensively employed in SCADA systems of different industry sectors in various geographical regions. Interoperability, both with the currently installed and future expansion with devices and systems, requires conformance to standards and compatibility testing for DNP3.
The SCADA systems may need to grow over time due to additional devices and data points. One would design the system to be scalable by specifying hardware and software components that can grow with the system. This may mean using or migrating the communication protocols and network infrastructure to scalable ones.
Performance optimization means minimizing latency in retrieving data or issuing responses to control commands. Network bandwidth, device processing capability, and protocol efficiency-eg, the efficiency with which DNP3 uses bandwidth-become key determinants in achieving desired levels of performance.
Ease of configuration, monitoring, and maintenance of the SCADA system drives operational efficiency and uptime. Native features of DNP3 include support for remote configuration and diagnostics that simplify many regular management tasks.
Industry-specific utilities, oil and gas, transportation, among other SCADA systems, should be compatible with regulatory requirements on data handling, safety, and environmental standards. The regulatory requirements have to be factored in at the design stage to ensure that the legal requirements on compliance are adhered to.
By carefully weighing these factors in the design phase, SCADA system designers are able to arrive at robust and efficient systems that effectively tap the potential of the DNP3 protocol.

July 25, 2025
The world energy scene is being revolutionized by the fast-paced increase of decentralized renewable energy sources like rooftop solar, wind microturbines, and energy storage in batteries. batteries. The driving force…
Know More
July 25, 2025
Smart metering has evolved significantly over the last two decades as it became a building block of modern energy management solutions. At the core of the evolution is the DLMS/COSEM…
Know More
July 25, 2025
As the energy sector undergoes rapid digital transformation, smart metering has emerged as a foundational technology in modern utility networks. By enabling real-time monitoring, automated billing, and remote disconnection, smart…
Know More