Unlocking the Power of AMI 2.0 and Meter Collars: A Utility Guide to Boosting DER Adoption and Grid Stability
Shwetha Bhat January 3, 2025
Shwetha Bhat January 3, 2025

The increasing integration of distributed energy resources (DERs) into the power grid presents significant challenges for grid management and optimization. Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) 2.0, with its enhanced communication and data processing capabilities, acts as a platform for effectively integrating residential and C&I consumer DERs. This application note explores the features and benefits of a comprehensive suite of Grid Edge applications designed to leverage AMI 2.0 and address challenges, focusing on enhancing grid visibility, flexibility, optimizing DER integration, and improving power quality monitoring. Additionally, it explores the alternative of using meter collars with AMI 1.0/smart meters to achieve similar benefits.
Introduction
The power grid is rapidly evolving, with a growing emphasis on clean energy sources and the integration of DERs such as solar PV systems, energy storage, and electric vehicles (EVs). Grid Edge, with enhanced communication and data processing capabilities, is crucial for the effective integration of DERs into the grid. This whitepaper explores a solution designed to leverage AMI 2.0 or Meter Collar to address the challenges posed by the growing influx of DERs.
Problem Statement
Utilities face numerous challenges in managing the increasing penetration of DERs into the distribution grid. These challenges include:
The Grid Edge application detailed below can address these pain points and provide valuable solutions for utilities and customers.
Grid Edge Applications
Consumer Indexing to LV Grid
Maintaining an accurate and up-to-date mapping of meters to their corresponding secondary transformers is crucial for grid optimization and planning. Manual verification of connections and phase information can be time-consuming and error prone.
A software application that comprises of an edge component and a cloud component that automates the process of consumer indexing to uniquely identify and categorize based on the phase of a distribution transformer (DT) they are connected to by comparing existing records with real-time data collected from smart meters. The application identifies discrepancies and provides updated indexing information, including phase details and transformer consumer is connected to.
Benefits:
Dynamic Hosting Capacity Insight
Determining the hosting capacity of a distribution network for DERs is essential to effectively manage DER adoption and grid stability. Traditional methods rely on static capacity calculations, which may not accurately reflect real-time grid conditions due to the presence of bi-directional power flow caused by the DERs.
Dynamic hosting capacity insight application leverages real-time data from smart meters and DERs to provide up-to-date capacity assessments. The application considers factors such as voltage limits, transformer ratings, and DER generation to provide accurate and dynamic hosting capacity insights.
Benefits:
DER/DR Gateway Application
Integrating DERs and flexible demand assets into the grid requires seamless communication and interoperability between devices and utility systems. Managing and controlling these DERs effectively is crucial for grid stability and efficiency.
DER gateway application acts as a communication hub for various DERs such as inverters for PV and BESS, EV chargers and flexible loads, facilitating data collection, control, and management. The gateway supports multiple communication protocols, enabling interoperability between diverse DER devices and utility systems.
Benefits:
Disaggregation of Distributed Generation and Loads
Understanding the individual contributions of different DERs at a site can be challenging, especially when they are not directly monitored. Disaggregated DER data is valuable for load profiling, grid planning, and customer insights.
A DER disaggregation solution that utilizes machine learning and advanced analytics to estimate the individual contributions of various DERs at a site, analyzes high-resolution meter data to identify and segregate DER generation patterns.
Benefits:
Power Quality Monitoring
Maintaining acceptable power quality levels is crucial for grid stability and customer satisfaction. Identifying and mitigating power quality issues caused by DERs, such as voltage fluctuations and harmonic distortions, is essential.
Power quality monitoring application that leverages real-time data from smart meters and DERs to detect and analyze power quality events, correlates these events with DER operation or EV charge usage to identify potential causes and facilitate proactive mitigation.
Benefits:
Solution
Solution Option 1: Using AMI 2.0 Meter
The solution detailed in this paper is used for integrating DERs into the grid ecosystem and has the following aspects:
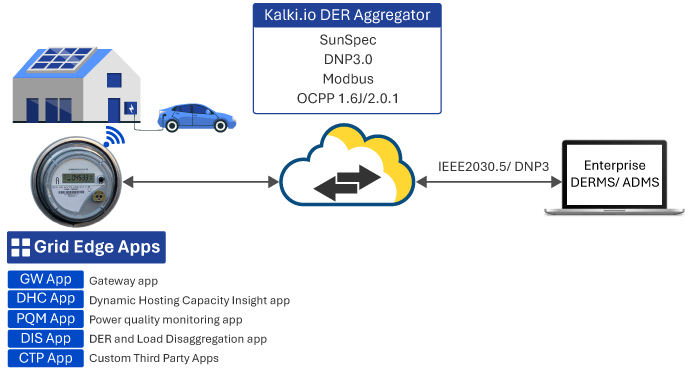
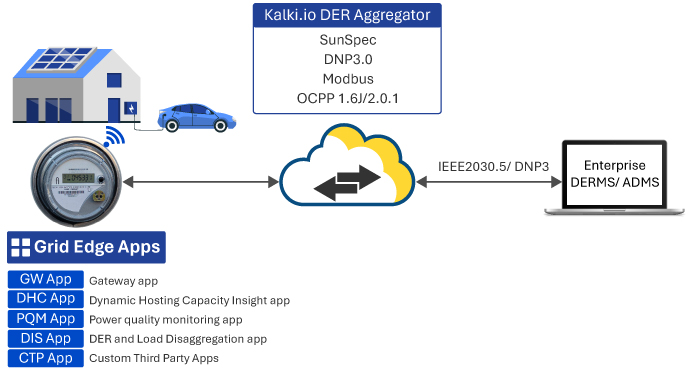
Data Collection and Aggregation:
The smart meter acts as the primary data source, capturing high-resolution metrological data, load profiles, and event data. A gateway app within the meter connects to the consumers’ WiFi network to which the DERs and flexible loads are connected. It collects telemetry data from behind-the-meter DERs, such as solar PV systems, batteries, and EVs.
Edge Analytics: An edge analytic application processes high-frequency data to compute relevant metrics every 15 minutes. In cases where DERs are not directly connected, a DER data disaggregation application within the edge computing environment estimates DER generation telemetry.
Cloud-Based Applications: A data hub, hosted in the cloud, receives and stores the aggregated data from the edge. Applications residing in the cloud analyze the data to derive detailed insights, including load and generation data, voltage levels, hosting capacity assessments, and fault/event data.
User Interface and Visualization: Analyzed insights are presented to users through a graphical user interface (GUI) with dashboards, charts, and other visual aids.
Solution Option 2: Using Meter Collar with AMI 1.0 / Smart Meters
Meter collars can serve as a complementary solution to AMI 2.0, or as a cost-effective alternative to enhance the capabilities of existing AMI 1.0 or smart meter deployments, particularly for integrating DERs in scenarios where direct AMI integration is not feasible.
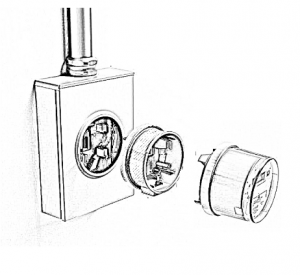
Advantages of Meter Collars
Simplified DER Connection: Meter collars provide a standardized and straightforward method, reducing installation complexity and costs.
Enhanced Data Acquisition: Meter collars are equipped with processing modules to run edge software applications to collect real-time data on DER generation, consumption, and grid parameters. This data can complement AMI data and provide additional insights into DER performance and grid impacts.
Cost-Effective Solution: Meter collars offer a cost-effective solution for integrating DERs, especially for residential and small commercial applications where the cost of AMI integration may be prohibitive.
Upgrading AMI 1.0 capabilities: For utilities with existing AMI 1.0 infrastructure, meter collars provide a pathway to gain benefits of AMI 2.0 without requiring a full system upgrade.
Kalki.io Capabilities
Kalki.io’s DER Aggregator is designed to make the aggregation and management of Distributed Energy Resources easier while ensuring robust security and advanced control features. It uses state-of-the-art encryption and authentication protocols to protect communications and data integrity, making it a reliable platform for sensitive energy operations. The in-band registration feature simplifies device onboarding by enabling seamless integration of DERs directly within the communication channel, reducing setup complexity and enhancing scalability. The scheduled control functionality enables exact, automated DER operation management based on pre-specified schedules, thereby optimizing the distribution of energy and satisfying grid demands. These features place Kalki.io as a secure, efficient, and user-friendly solution for modern energy management.
Benefits for Utilities
This approach establishes a data pipeline, starting from behind the meter assets through the smart meter, passing through edge analytics, and culminating in the cloud-based data hub. The solution processes the data and delivers actionable insights to users via an intuitive GUI, enabling real-time monitoring, analysis, and optimization of DER integration within the grid.
The proposed solution offers several benefits for utilities:
Benefits for Consumers
The solution also offers benefits for customers:
Conclusion
The suite of Grid Edge applications, in conjunction with AMI 2.0 and meter collars, offers a powerful and comprehensive solution for managing the growing influx of DERs into the grid. By providing enhanced grid visibility, optimized DER integration, and improved power quality monitoring, these applications enable utilities to effectively navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by the evolving energy landscape. The solution also empowers customers with improved reliability, increased DER adoption, and personalized insights, contributing to a cleaner, more resilient, and customer-centric grid.

July 25, 2025
The world energy scene is being revolutionized by the fast-paced increase of decentralized renewable energy sources like rooftop solar, wind microturbines, and energy storage in batteries. batteries. The driving force…
Know More
July 25, 2025
Smart metering has evolved significantly over the last two decades as it became a building block of modern energy management solutions. At the core of the evolution is the DLMS/COSEM…
Know More
July 25, 2025
As the energy sector undergoes rapid digital transformation, smart metering has emerged as a foundational technology in modern utility networks. By enabling real-time monitoring, automated billing, and remote disconnection, smart…
Know More